Supreme Court Term 2025-2026
We’re breaking down the cases we've asked the court to consider this term.
Latest Case Updates
Ongoing
Updated February 25, 2026
Ongoing
Updated February 18, 2026
Ongoing
Updated January 26, 2026
Ongoing
Updated January 16, 2026
Featured
Missouri
Feb 2026

Voting Rights
Missouri v. U.S. Department of Commerce
A coalition of civil rights and immigrant-rights organizations has moved to intervene as defendants in a lawsuit that threatens to dismantle the Constitution‚Äôs long-standing requirement that the decennial census count all people living in the United States. Missouri asks the court to exclude undocumented immigrants and people living in the country on temporary visas from the census count used to determine congressional representation‚ÄĒan unprecedented move that would upend more than two centuries of constitutional practice.
Mississippi
Dec 2025
Voting Rights
White v. Mississippi State Board of Elections
District lines used to elect Mississippi’s Supreme Court have gone unchanged for more than 35 years. We’re suing because the current lines crack the Mississippi Delta and dilute the voting strength of Black Mississippians in state Supreme Court elections, in violation of the Voting Rights Act.
Court Case
Dec 2025

National Security
Human Rights
FOIA Case Seeking the Trump Administration’s Legal Justification for Deadly Boat Strikes
The Department of Justice‚Äôs Office of Legal Counsel (‚ÄúOLC‚ÄĚ) authored a legal opinion that reportedly claims to justify the Trump administration‚Äôs illegal lethal strikes on civilians in boats in the Caribbean Sea and eastern Pacific Ocean. Media reports indicate that, in addition to claiming that the strikes are lawful acts in an alleged ‚Äúarmed conflict‚ÄĚ with unspecified drug cartels, the OLC opinion also purports to immunize personnel who authorized or took part in the strikes from future criminal prosecution. Because the public deserves to know how our government is justifying these illegal strikes, and why they think the people who carried them out should not be held accountable, the ļž–” ”∆Ķ is seeking immediate release of the OLC legal opinion and related documents pursuant to the Freedom of Information Act.
U.S. Supreme Court
Dec 2025

Immigrants' Rights
Barbara v. Donald J. Trump
President Trump is attempting to undermine the promise of birthright citizenship to children born on U.S. soil. But the ļž–” ”∆Ķ and partners are fighting to protect the rights of citizens that are plainly stated in the Constitution, federal statute, and reaffirmed by the Supreme Court for more than a century. We‚Äôre arguing against the Trump administration in the Supreme Court and are confident we will win.
U.S. Supreme Court
Nov 2025
Voting Rights
Racial Justice
Allen v. Milligan
Whether Alabama’s congressional districts violate Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act because they discriminate against Black voters. We succeeded in winning a new map for 2024 elections which, for the first time, has two congressional district that provide Black voters a fair opportunity to elect candidates of their choosing despite multiple attempts by Alabama to stop us at the Supreme Court. Despite this win, Alabama is still defending its discriminatory map, and a trial was held in February 2025 to determine the map for the rest of the decade.
In May 2025, a federal court ruled that Alabama's 2023 congressional map both violates Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act and was enacted by the Alabama Legislature with racially discriminatory intent.
Washington, D.C.
Oct 2025

Voting Rights
League of Women Voters Education Fund v. Trump
On March 25, 2025, in a sweeping and unprecedented Executive Order, President Trump attempted to usurp the power to regulate federal elections from Congress and the States. Among other things, the Executive Order directs the Election Assistance Commission‚ÄĒan agency that Congress specifically established to be bipartisan and independent‚ÄĒto require voters to show a passport or other citizenship documentation in order to register to vote in federal elections. If implemented, the Executive Order would threaten the ability of millions of eligible Americans to register and vote and upend the administration of federal elections.
On behalf of leading voter registration organizations and advocacy organizations, the ļž–” ”∆Ķ and co-counsel filed a lawsuit to block the Executive Order as an unconstitutional power grab.
U.S. Supreme Court
Oct 2025
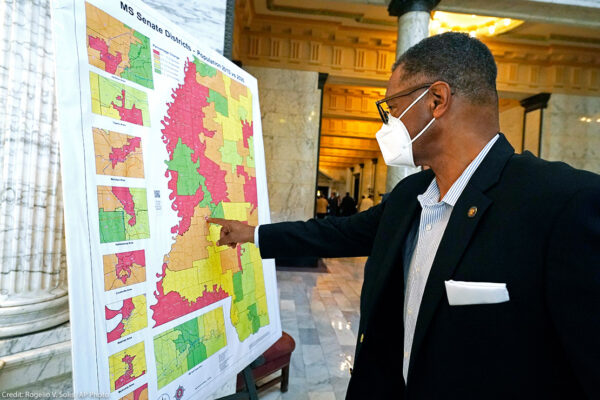
Voting Rights
State Board of Election Commissioners v. Mississippi State Conference of the NAACP
Mississippi has a growing Black population, which is already the largest Black population percentage of any state in the country. Yet. Black Mississippians continue to be significantly under-represented in the state legislature, as Mississippi’s latest districting maps fail to reflect the reality of the state’s changing demographics. During the 2022 redistricting process, the Mississippi legislature refused to create any new districts where Black voters have a chance to elect their preferred representative. The current district lines therefore dilute the voting power of Black Mississippians and continue to deprive them of political representation that is responsive to their needs and concerns, including severe disparities in education and healthcare.
U.S. Supreme Court
Oct 2025
Voting Rights
Louisiana v. Callais (Callais v. Landry)
Whether the congressional map Louisiana adopted to cure a Voting Rights Act violation in Robinson v. Ardoin is itself unlawful as a gerrymander.
Missouri
Sep 2025

Voting Rights
Wise v. Missouri
In unprecedented fashion, the State of Missouri has redrawn the district lines used for electing members of Congress for a second time this decade. These new district lines are gerrymandered and will harm political representation for all Missourians, particularly Black residents in Kansas City, who have been divided along racial lines.
All Cases
1,678 Court Cases

North Carolina
May 2025
Voting Rights
Griffin v. North Carolina Board of Elections (Amicus)
This case arises from the November 2024 election for state supreme court justice in North Carolina. Incumbent State Supreme Court Justice Allison Riggs defeated Court of Appeals Judge Jefferson Griffin, but Griffin has filed a petition seeking to invalidate more than 60,000 votes from the election. He argues that the state Board of Elections impermissibly allowed over 60,000 people to register without providing their driver‚Äôs licenses or social security numbers, and that the Board impermissibly allowed thousands of overseas voters to cast absentee ballots without photo identification. The petition has resulted in both federal and state litigation, and the ļž–” ”∆Ķ has submitted amicus briefs in both venues. In the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit, the ļž–” ”∆Ķ‚Äôs Voting Rights Project and the ļž–” ”∆Ķ of North Carolina filed an amicus brief explaining that the petition‚Äôs attempt to cancel tens of thousands of votes threatens democratic backsliding in North Carolina. Separately, in the North Carolina Court of Appeals, the ļž–” ”∆Ķ‚Äôs State Supreme Court Initiative and the ļž–” ”∆Ķ of North Carolina submitted an amicus brief explaining that, even if the Board did make mistakes, cancelling votes as a consequence of those mistakes would violate the popular sovereignty provision of the North Carolina Constitution because voters relied on the Board to know how to register and vote.
Explore case
North Carolina
May 2025

Voting Rights
Griffin v. North Carolina Board of Elections (Amicus)
This case arises from the November 2024 election for state supreme court justice in North Carolina. Incumbent State Supreme Court Justice Allison Riggs defeated Court of Appeals Judge Jefferson Griffin, but Griffin has filed a petition seeking to invalidate more than 60,000 votes from the election. He argues that the state Board of Elections impermissibly allowed over 60,000 people to register without providing their driver‚Äôs licenses or social security numbers, and that the Board impermissibly allowed thousands of overseas voters to cast absentee ballots without photo identification. The petition has resulted in both federal and state litigation, and the ļž–” ”∆Ķ has submitted amicus briefs in both venues. In the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit, the ļž–” ”∆Ķ‚Äôs Voting Rights Project and the ļž–” ”∆Ķ of North Carolina filed an amicus brief explaining that the petition‚Äôs attempt to cancel tens of thousands of votes threatens democratic backsliding in North Carolina. Separately, in the North Carolina Court of Appeals, the ļž–” ”∆Ķ‚Äôs State Supreme Court Initiative and the ļž–” ”∆Ķ of North Carolina submitted an amicus brief explaining that, even if the Board did make mistakes, cancelling votes as a consequence of those mistakes would violate the popular sovereignty provision of the North Carolina Constitution because voters relied on the Board to know how to register and vote.

U.S. Supreme Court
May 2025
Civil Liberties
APHA v. NIH
APHA v. NIH is a legal challenge to the unprecedented and ideologically-driven purge of hundreds of biomedical research projects by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Years of research on a wide span of critical health issues has been abruptly cancelled, as have grants and programs designed to address the underrepresentation of racial minorities, women, and economically disadvantaged scientists in the biomedical field.
Explore case
U.S. Supreme Court
May 2025

Civil Liberties
APHA v. NIH
APHA v. NIH is a legal challenge to the unprecedented and ideologically-driven purge of hundreds of biomedical research projects by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Years of research on a wide span of critical health issues has been abruptly cancelled, as have grants and programs designed to address the underrepresentation of racial minorities, women, and economically disadvantaged scientists in the biomedical field.

Georgia
May 2025
Criminal Law Reform
Smart Justice
Coronell, et al. v. Georgia
As a result of Georgia Senate Bill 63, thousands of people are being kept in jail pre-trial because they can‚Äôt afford to post bail, even when a judge believes the person should have been released until trial with no risk to the public. The ļž–” ”∆Ķ‚Äôs Criminal Law Reform Project, along with ļž–” ”∆Ķ-GA and the Southern Center for Human Rights, filed a class action lawsuit challenging SB63‚Äôs mandatory monetary bail provisions under the Georgia State Constitution.
Explore case
Georgia
May 2025

Criminal Law Reform
Smart Justice
Coronell, et al. v. Georgia
As a result of Georgia Senate Bill 63, thousands of people are being kept in jail pre-trial because they can‚Äôt afford to post bail, even when a judge believes the person should have been released until trial with no risk to the public. The ļž–” ”∆Ķ‚Äôs Criminal Law Reform Project, along with ļž–” ”∆Ķ-GA and the Southern Center for Human Rights, filed a class action lawsuit challenging SB63‚Äôs mandatory monetary bail provisions under the Georgia State Constitution.

Vermont
Apr 2025
Free Speech
Immigrants' Rights
Mahdawi v. Trump
Whether a lawful permanent resident of the U.S. can be arrested and detained on the basis of their political speech and advocacy.
Explore case
Vermont
Apr 2025

Free Speech
Immigrants' Rights
Mahdawi v. Trump
Whether a lawful permanent resident of the U.S. can be arrested and detained on the basis of their political speech and advocacy.

Washington, D.C.
Apr 2025
Immigrants' Rights
National Security
Las Americas Immigrant Advocacy Center v. Noem
Immigrants’ rights advocates sued the Trump administration on Feb. 12, 2025, for access to immigrants transferred from the United States to detention at Guantánamo Bay in Cuba under President Trump’s recent order.
Explore case
Washington, D.C.
Apr 2025

Immigrants' Rights
National Security
Las Americas Immigrant Advocacy Center v. Noem
Immigrants’ rights advocates sued the Trump administration on Feb. 12, 2025, for access to immigrants transferred from the United States to detention at Guantánamo Bay in Cuba under President Trump’s recent order.
